Background downloads and uploads in Windows 10 can be easily found with the Windows Task Manager and Windows Resource Monitor.
When you are trying to fix a slow internet connection, you should at first always look out for background downloads on your PC or notebook. It is often that some applications are currently downloading updates or patches in the background. Most of the applications with a background downloading functionality are configured to use the complete available bandwidth. This slows down your internet connection.
Using Windows Task Manager to find a background download
Windows’ Task Manager has always been the number one tool to fix issues with program. Even if it had only been used for killing hanging application. With Windows 8 the Task Manager got a new feature for showing the network usage of an application. You can use this feature to identify the application which consumes the most bandwidth on your local PC.
Press Ctrl+Alt+Del and in the appearing screen click on Task Manager. The Windows 10 Task Manager opens.
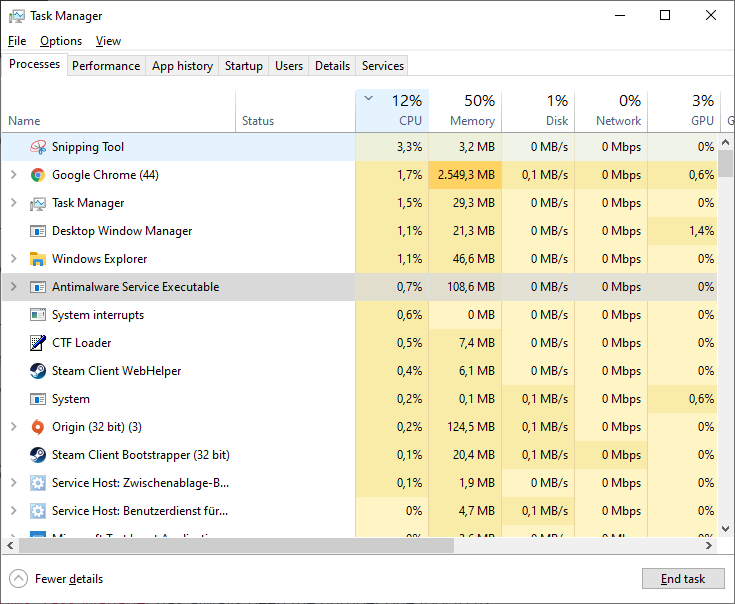
Click on the Network column to sort all applications by the network bandwidth usage:
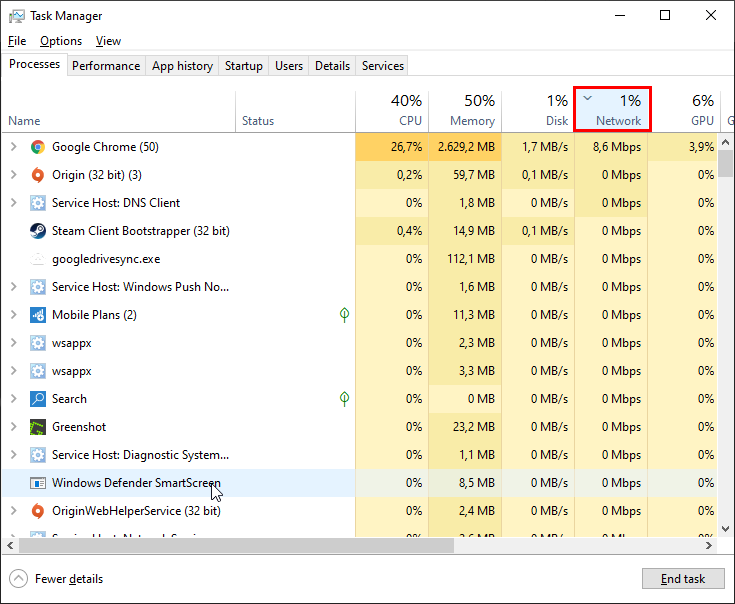
In the screenshot above you can see that Google Chrome uses 8.6 MBit/s (8.6 Mbps) of the available bandwidth of my internet connection. It is important that you don’t judge by the relative percentage numbers in the Network’s header cell! In my case this is 1%. Windows calculates the relative usage based upon the underlying hardware. My PC has 1000 MBit/s (1 GBit/s) network adapter which is connected to a WiFi router with an 32 MBit/s (32 Mbit/s) internet connection. The 1% is only relative to my network adapter but almost 25% of my internet connection
Stop the application from downloading in the background
After you have identified the application, you can try to stop or throttle the background download.
- How to stop Valve’s Steam from downloading in the background
- How to stop EA’s Origin from downloading in the background
- For Service Host: Windows Update Service there is no easy way to prevent the download. You might want to change the maximum available bandwidth for Windows Updates
- For other applications, make a right click on the corresponding application in the Windows Task Manager and select End Task.
Using Resource Monitor to get a more detailed view
In addition to the Windows Task Manager, the Resource Monitor can also be used to get a more detailed view. Besides from applications doing background downloads there might be also applications which are uploading data back to the internet. If you are using tools like Dropbox, Google Drive or Microsoft OneDrive, there will be regulary background uploads for your local backups or synchronized files.
With Windows Resource Monitor you can see, which application uses how much of your download and upload bandwidth.
To start the Resource Monitor, in the Task Manager click on the Performance tab. Then click on Resource Monitor:

In the opening window, click on the Network tab:

In the lower panel, you can click on the Send and Receive colum to sort it ascending or descending:
- Send shows how much of your upload bandwidth is used.
- Receive shows, how much of your download bandwidth is used.
Find the corresponding application
The Image column contains the name of the executable. In some cases the meaning is obvious but not always. Make a note of the number in the PID column and switch back to the Task Manager’s Processes tab. Right click on the table header (e.g on Name or Status) and select PID.
Now you can correlate the internal PID with the named application.
Check your PC or notebook for virus or malware
You have checked that nothing on your PC or notebook downloads or uploads from it but Windows still eats your Internet bandwidth in the background? This might be a sign for a virus or malware infection. Depending on the type of virus or malware they can hide from the Task Manager and the calculated network usage.
In this case, do a full anti virus check.